Supporters of former President Donald Trump have been utilizing AI-generated deepfake images featuring Black voters to promote the idea of African Americans endorsing the Republican, as uncovered by BBC Panorama.
The deepfakes, which manipulate visuals using artificial intelligence, portray Black individuals as Trump supporters, potentially aiming to influence a political narrative and help increase support for Trump among an elusive demographic.
While Trump has actively sought the support of Black voters, there is no direct evidence linking these manipulated images to his official campaign. The AI-generated deepfakes represent an emerging disinformation trend leading up to the presidential election in November.
BBC Panorama discovered several instances of such manipulated images, with one example involving a conservative radio show host, Mark Kaye, and his team in Florida. They created an image showing Trump with a group of Black women, which was shared on Facebook.
You can see it below.
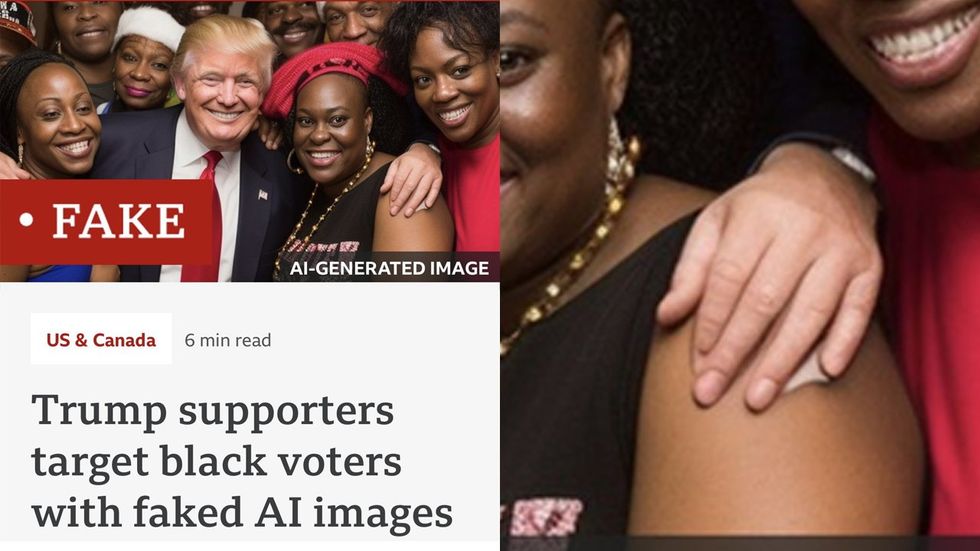
Another photo shows Trump posing with Black voters on a front porch, initially posted by a satirical account and later reposted with a false caption.
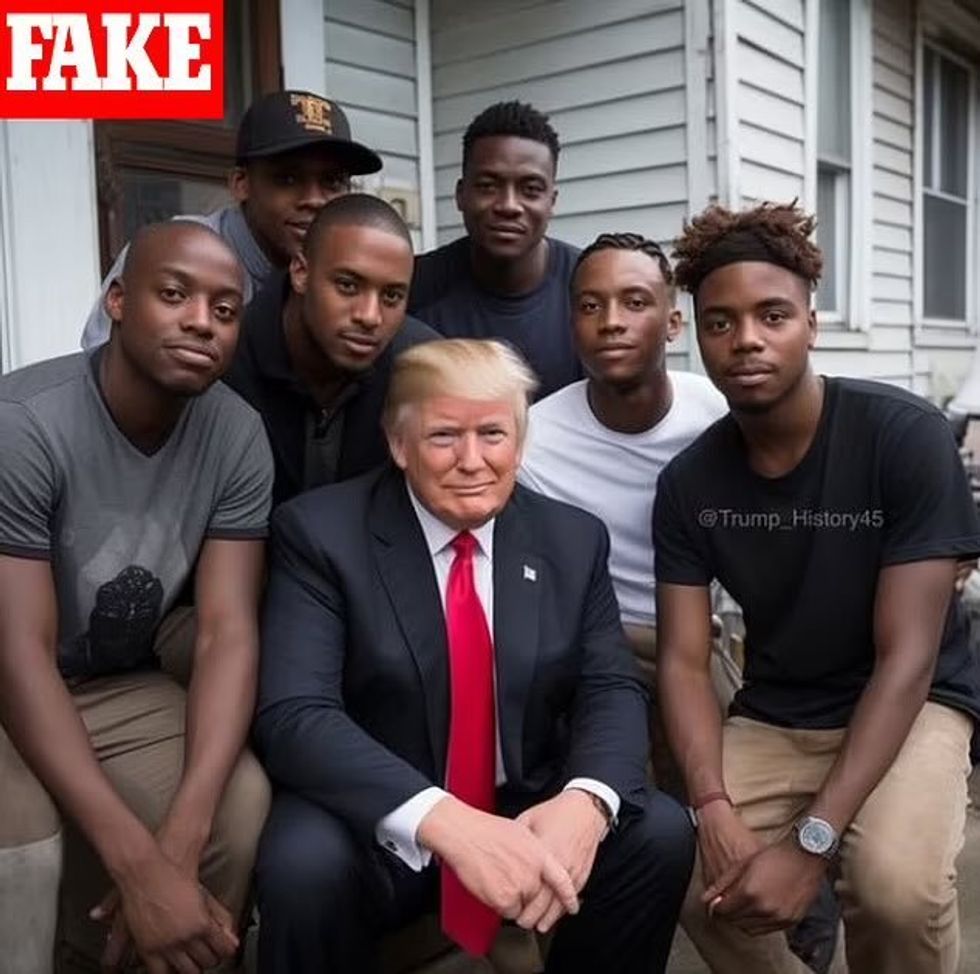

Although the images initially appears real, close examination reveals telltale signs of AI manipulation, such as unnaturally shiny skin and missing fingers.
Kaye admitted that the image was not accurate but defended its use as a storytelling technique:
"I'm not claiming it is accurate. I'm not saying, 'Hey, look, Donald Trump was at this party with all of these African American voters. Look how much they love him!'"
"If anybody's voting one way or another because of one photo they see on a Facebook page, that's a problem with that person, not with the post itself."
These findings prompted criticism from individuals like liberal activist Ron Filipkowski, the editor-in-chief of MeidasTouch, who said it was "not surprising" that when BBC reporter Marianna Spring conducted her investigation and tracked down the individuals who created some of the images "they were white guys who blocked her."
The news sparked significant commentary online, with many pointing out how AI-generated deepfakes are being employed to spread misinformation and disinformation during the ongoing election cycle.
Recent findings from a New York Times and Sienna College poll revealed a notable shift in Black voter support for President Joe Biden in key swing states.
In six crucial swing states, 71% of Black voters indicated support for Biden in 2024, a significant decrease from the 92% national support that contributed to his victory in the previous election. This shift has prompted concerns and discussions about disinformation tactics, particularly the use of AI-generated deepfakes targeting Black voters.
Cliff Albright, co-founder of the campaign group Black Voters Matter, emphasized the consistency of the fake images with a "very strategic narrative" orchestrated by conservatives, spanning from the Trump campaign to online influencers.
This narrative aims to sway Black voters, with a particular focus on young Black men, who are perceived to be more receptive to supporting Trump than Black women. MAGA Inc, the primary political action committee supporting Trump, recently launched an advertising campaign targeting Black voters in key states like Georgia, Michigan, and Pennsylvania.








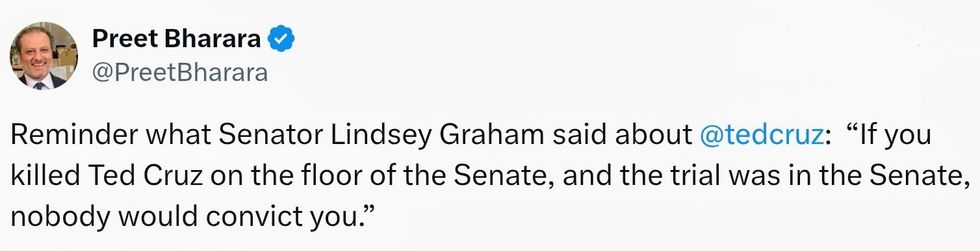 @PreetBharara/X
@PreetBharara/X @RepBrendanBoyle/X
@RepBrendanBoyle/X @twesq/Bluesky
@twesq/Bluesky @christopherharris/Bluesky
@christopherharris/Bluesky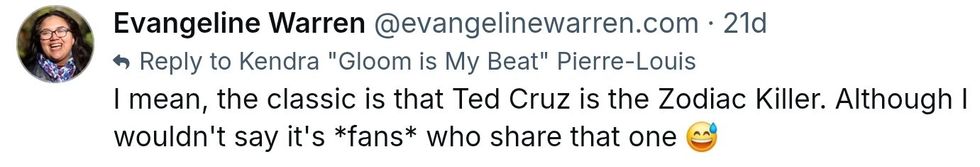 @evangelinewarren/X
@evangelinewarren/X





 @FrankC164/X
@FrankC164/X
 AMC
AMC