Your smile: it's probably not something you think about very much.
For people whose facial muscles work properly, a smile is just something that happens.
But for people who suffer from facial paralysis, or have suffered a major injury to their face, it's not so easy.
Not being able to smile can cause major breakdowns in communication that can lead to anxiety and depression. "Facial paralysis often results in a cycle of isolation because patients can't interact with others as they used to," researcher Nathaniel Helwig told the University of Minnesota's CLAgency.
Scientists sought to understand what makes up a great smile so they can better help patients who undergo facial reanimation surgery. There is a fine line between a smile and a grimace, especially if the muscles around the eyes are also paralyzed. Our eyes convey much of the emotion involved in a smile.
How to smile without looking like a creepwww.youtube.com
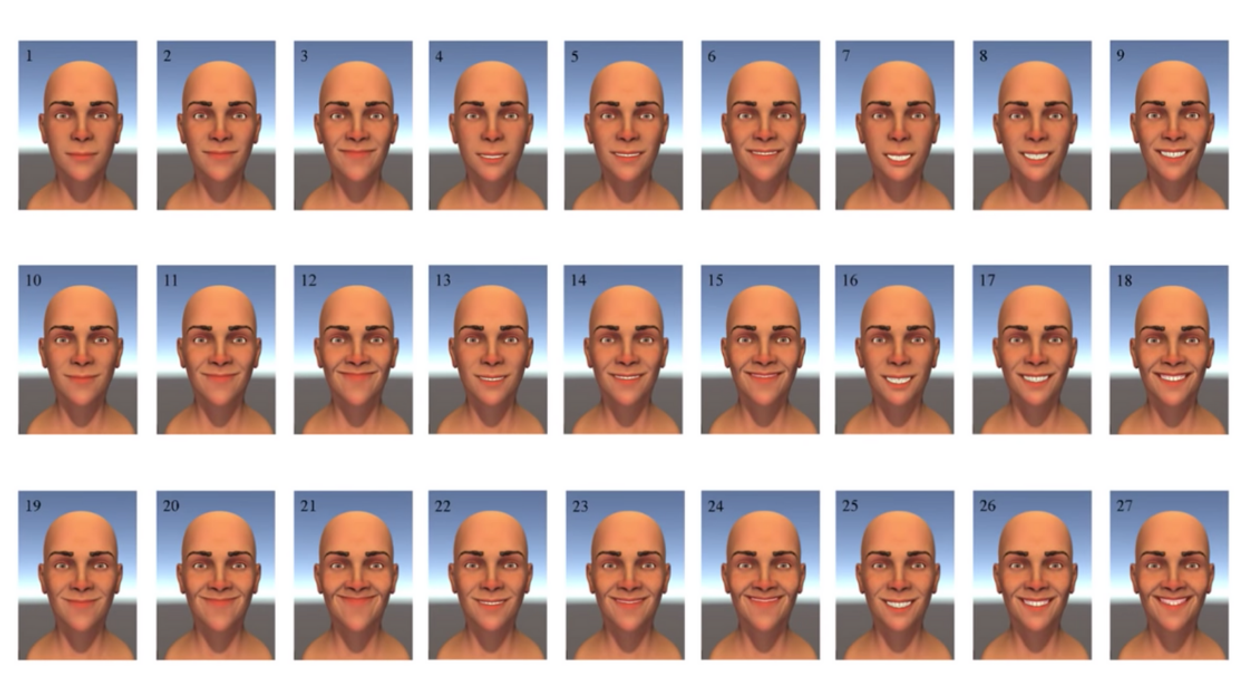
Using a computer model, researchers from the University of Minnesota created 27 different smiles and showed them to over 800 people at the Minnesota State Fair. The smiles were changed based on 4 variables: angle, width, toothiness, and degree of crookedness. Viewers rated each smile on 4 variables as well: effectiveness, genuineness, pleasantness, and the emotion expressed.
The models were shown to participants as animated clips, to closer mimic the experience of seeing someone smile.
Thee research team consisted of researchers from multiple disciplines including: psychology, computer sciences and engineering, statistics, and otolaryngology (head and neck specialists). They announced their results in a paper (available here on PLOS ONE) in June of 2017.
Because facial reanimation surgeries can't do much to restore movement to the area around a person's eyes, the eyes on each computer modeled smile were left exactly the same.
Researchers found that smiles with a medium width tended to be rated higher. Wide, upturned smiles that showed a lot of teeth had the lowest ratings. Smiles with a medium upturn were rated higher, whereas very upturned (v-shaped) smiles tended to be seen as disturbing instead.
Wide open smiles that show a lot of teeth were easily mistaken for anger or contempt, so the smiles that showed less teeth were rated higher. Slightly crooked smiles were rated better, but those that were extremely uneven were unpopular.
Sofia Sofia Lyford Pike, MD, who is the senior author of the study and an assistant professor within the University of Minnesota Medical School said:
"People may think this is merely a vanity test, but it has major implications for how we work with patients that have facial paralysis. By knowing how society perceives facial motion and smiles, we can work with our patients to recover in a way that will enhance their interactions with others and improve quality of life."
Co-author Nathaniel Helwig stressed the importance of the study as well when he spoke to ResearchGate.
"Partial facial paralysis robs an individual of their ability to smile, which can have significant psychological and social consequences. To improve outcomes for these individuals, it is imperative to have a detailed understanding of what exactly constitutes a 'successful smile."
On the motivation for their research, Helwig said:
"Sofia Lyford-Pike, a facial plastic and reconstructive surgeon, wanted to know how to create the perfect smile for her patients, in order to help them better reintegrate back into society after a stroke, disease, or injury. To discover the perfect smile, she sought out the help of Stephen Guy, a computer scientist, and myself, a psychologist and statistician. Together, we designed an experiment to determine which combinations of spatial and temporal features join to create successful smiles."
This research will go a long way in helping surgeons like Pike create better smiles for patients.









 @RepOgles/X
@RepOgles/X @RepOgles/X
@RepOgles/X




 @chrisbrownofficial/Instagram
@chrisbrownofficial/Instagram u/oatlatt/Reddit
u/oatlatt/Reddit u/LoveTheAhole/Reddit
u/LoveTheAhole/Reddit u/SoFetch89/Reddit
u/SoFetch89/Reddit u/00trysomethingnu/Reddit
u/00trysomethingnu/Reddit u/kittybuscemi/Reddit
u/kittybuscemi/Reddit u/___nic/Reddit
u/___nic/Reddit u/WaterMagician/Reddit
u/WaterMagician/Reddit u/west-brompton/Reddit
u/west-brompton/Reddit u/GhostlySpinster/Reddit
u/GhostlySpinster/Reddit u/Asleep_Tap6199/Reddit
u/Asleep_Tap6199/Reddit u/afreudtolove/Reddit
u/afreudtolove/Reddit u/myfriendtoldmetojoin/Reddit
u/myfriendtoldmetojoin/Reddit
 @charlesbeckinsale/Instagram
@charlesbeckinsale/Instagram @liamgriffin/Instagram
@liamgriffin/Instagram @valentinoguseli/Instagram
@valentinoguseli/Instagram @17is/Instagram
@17is/Instagram @torahbright/Instagram
@torahbright/Instagram @mcfetridge/Instagram
@mcfetridge/Instagram @colleenquigley/Instagram
@colleenquigley/Instagram @jonathanwaynefreeman/Instagram
@jonathanwaynefreeman/Instagram
 @amberglenniceskater/Instagram
@amberglenniceskater/Instagram