Platypus milk contains special proteins that have the potential to combat the growing world-wide problem of antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria, known as "superbugs," are on the rise across the world in a micro-evolutionary response to decades of antibiotic use to fight bacterial infections. Superbugs arise from genetic mutations in bacterial DNA—a direct consequence of exposure to antibiotics in microbe populations. It's evolution and artificial selection in action, and superbugs are becoming an increasing risk to human and animal health across the planet. Because superbug infections don't respond to conventional antibiotics, researchers have been scrambling to find a solution to what could lead to catastrophic, widespread super-infections, much like how medieval Europe had no defense against the Bubonic Plague which wiped out a quarter of the population in the Middle Ages.
"They are duck-billed, egg-laying, semi-aquatic mammals with poisonous spurs on their webbed feet: the Australian platypus is so weird that early European zoologists thought it must be an elaborate hoax." - The Guardian
New research suggests that the strange nature of platypus and their milk, of all things, could be a key ally to doctors desperately seeking a cure for antibiotic resistant bacteria. In a study published in Structural Biology Communications, Australian biochemists, working in tandem with scientists at Deakin University, discovered that platypus milk contains special antibiotic properties, due to the unique way platypus lactate and nurse their young.
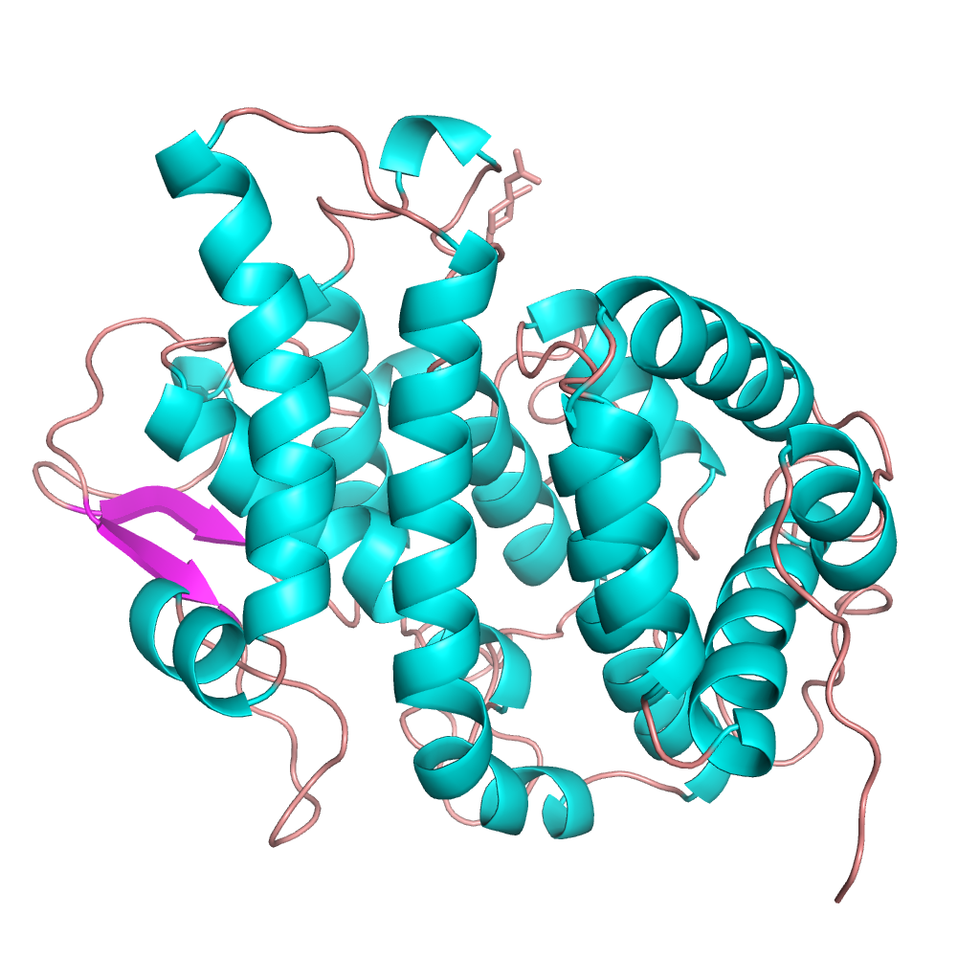
Lead researcher Janet Newman of the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) explains in her study that platypus don't have nipples or mammary glands like other mammals, because they belong to a small group of primitive mammals called monotremes. Monotreme milk is stored in the gut and then excreted through the skin. Because the milk sits in the gut, rather than in an independent system of glands, the milk is exposed to the environment, giving it, in some sense, antimicrobial and immunological properties.
"This special component has antibacterial properties against some of the nastier bugs you find in the environment but not against some bacteria found in the guts of the young," Newman said.
Newman and her team were able to identify that the protein structure of monotreme milk, found only in platypus, could be engineered to fight superbugs. Unlike their placental and marsupial mammalian cousins, monotremes are a small group of mammals that lay eggs, rather than giving birth to live young. Monotremes are a window into mammalian evolutionary history—over thousands of generations, most mammals evolved to form mammary glands, leaving little to no use for the ancient monotreme protein.
"Platypus are such weird animals that it would make sense for them to have weird biochemistry," Newman said in a statement. "By taking a closer look at their milk, we've characterized a new protein that has unique antibacterial properties with the potential to save lives."
The monotreme protein was named the "Shirley Temple" protein, due to its ringlet-like structure, resembling the hair of the 1930's child movie star of the same name. It's so unusual that the special fold in its molecular structure has never been identified in more than 100,000 other types of known proteins.
"That's interesting, because it's the shape of proteins which dictate their function," Newman explained. "So the hope is that the novel structure, in the best possible world, would eventually lead to a therapeutic that is based on a completely different way of dealing with microbial infections than our current antibiotics."
In 2014, the World Health Organization issued a stern warning that the world may be entering what it calls the "post-antibiotic era," where conventional antibiotics may be rendered ineffective against even the most common types of bacterial infections and injuries.
"Without urgent, coordinated action by many stakeholders, the world is headed for a post-antibiotic era, in which common infections and minor injuries which have been treatable for decades can once again kill," warned WHO's Assistant Director-General for Health Security Dr. Keiji Fukuda. "Effective antibiotics have been one of the pillars allowing us to live longer, live healthier, and benefit from modern medicine. Unless we take significant actions to improve efforts to prevent infections and also change how we produce, prescribe and use antibiotics, the world will lose more and more of these global public health goods and the implications will be devastating."















 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social

 @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram @c2e2/Instagram
@c2e2/Instagram