It is known by many names in popular culture: “hug drug,” “love drug,” “dance drug,” “ecstasy,” “XTC” and “Molly” — along with its scientific designation: MDMA. Now, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has bestowed an additional moniker: “breakthrough therapy.”
The FDA has announced that it is considering MDMA as a therapy to treat veterans with PTSD.
MDMA (or 3.4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) has a convoluted history. It was first developed by a chemist working for the Merck pharmaceutical company in 1912, originally intended to combat abnormal bleeding conditions. Later, Merck explored whether MDMA would function similar to adrenaline or ephedrine since MDMA and ephedrine have similar chemical structures.
Declassified documents have shown that the United States military experimented with the drug in the 1950s as a possible “truth serum” with unspecified outcomes. In the mid-1960s, a psychopharmacologist synthesized MDMA during a series of experiments while working for Dow Chemical. This scientist did not investigate its psychoactive capabilities until hearing reports of its recreational use a decade later.
The first report of non-medical recreational use of MDMA was in the early 1970s. It seems that Chicago was the first epicenter of MDMA drug use in the nightlife scene, which eventually spread to California, and then on to rest of the United States and the globe.
In 1976, Alexander Shulgin, the chemist who synthesized MDMA in the 1960s for Dow Chemical, tried it on himself and recommended the compound to fellow psychopharmacologists and psychotherapists. Two years later, he published a paper with another chemist named David Nichols detailing how MDMA affects humans, describing that it “appears to evoke an easily controlled altered state of consciousness with emotional and sensual overtones. It can be compared in its effect to marijuana, to psilocybin devoid of the hallucinatory component.” The exploding popularity of MDMA as a party drug around the globe led to several countries to illegalize it and classify it as a Schedule 1 substance including Great Britain and the United States.
Enter the modern era, where MDMA is being investigated by the scientific community for its utility in treating a number of psychiatric conditions, most notably post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
PTSD is a psychological condition that develops after an individual has experienced a severely traumatic event such as a car accident, near-death experience, warfare, or some form of assault. Symptoms usually persist for more than a month and can include but are not limited to: heightened “fight or flight” responses, severe avoidance of anything perceived as stressful, as well as emotional and physical distress when confronted with a potentially traumatic incident. Currently, only two drugs have been approved for treating PTSD (Paxil and Zoloft), which have unfortunately underperformed in alleviating PTSD for veterans. Thus, alternative treatments must be found to remedy the suffering of veterans afflicted with PTSD.
Fast forward to August of 2017: the FDA announced that it was classifying MDMA as a “breakthrough therapy” for the treatment of veterans experiencing PTSD.
The FDA rarely awards such a designation for substances that show “substantial improvement over existing therapies” in the treatment of severe conditions and diseases. This milestone was reached through the efforts of Rick Doblin, who founded the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (or MAPS). The mission of this organization has been to harness the medical applications of marijuana and psychedelic drugs. MAPS secured funding for the Phase 2 clinical trials for MDMA’s use as a psychotherapy for US military veterans.
To prevent any possible bias, the clinicians used a double-blind for the Phase 2 clinical studies, so neither the doctors nor the patients were aware who was receiving MDMA and who was being given a placebo.
Over the course of several months, three doses were administered. The results were encouraging, where one study saw two-thirds of the patients fully recover from their PTSD. As many as 88 percent of individuals who received the MDMA treatments remained free of the symptoms of PTSD for over three years after receiving their final dose. The better-than-expected results of the Phase 2 trials led the FDA to approve large-scale Phase 3 studies in late 2016 with an anticipated start in early to mid-2018. These clinical investigations will be the final phase in getting the FDA to designate MDMA as a “prescription drug.” According to MAPS, the earliest date such an approval could be given would be as early as 2021.
MDMA is not the only psychoactive drug being researched for its benefits to people coping with PTSD and a host of other psychological conditions.
Indeed, there have been very recent reports championing hallucinogenics like LSD and psilocybin mushrooms for treating PTSD. Beyond just PTSD, the use of psychedelic drugs such as MDMA and psilocybin has also been touted for palliative care in the treatment of those suffering from terminal ailments. It seems that MDMA has come full circle with regard to its therapeutic potential as in the 1970s when it was being promulgated by the psychiatric community as a drug capable of alleviating a variety of psychiatric conditions.
Despite all the research now showing its vast potential to help ameliorate multiple anxiety disorders, the stigma of it being nothing more than a “rave drug” for electronic music gatherings persists and with a significant amount of skepticism.
Indeed, the director of the Langone School of Medicine at New York University, Dr. Charles R. Marmar recently remarked that MDMA is “a feel-good drug, and we know people are prone to abuse it” after learning of the FDA green light for Phase 3 clinical trials. Still, MAPS scientists contend that the euphoric effect of the drug is what allows PTSD patients to circumvent mental barriers and confront the sources of their profound anxiety. The future utility of psychedelic drugs for medical use depends on the outcome of the current clinical trials, though the momentum seems to be on the side of the scientists and doctors committed to their therapeutic applications.







 @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram @therealjeffreyross/Instagram
@therealjeffreyross/Instagram








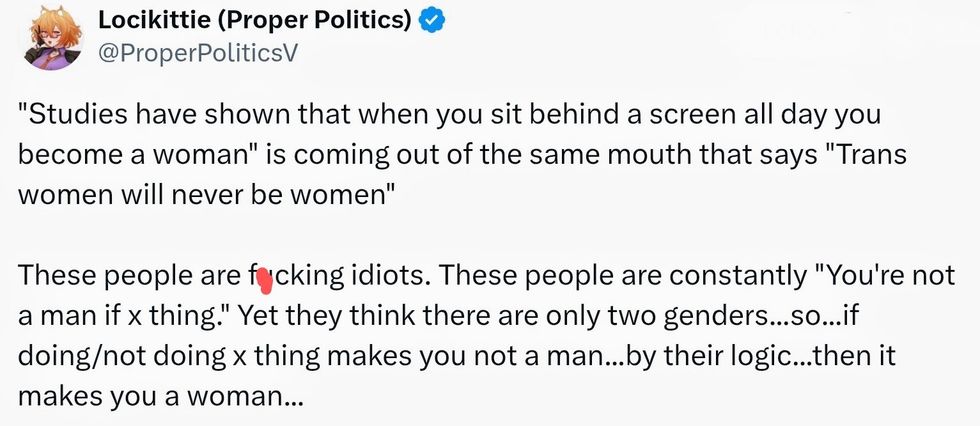
 @mikeredmond/Bluesky
@mikeredmond/Bluesky

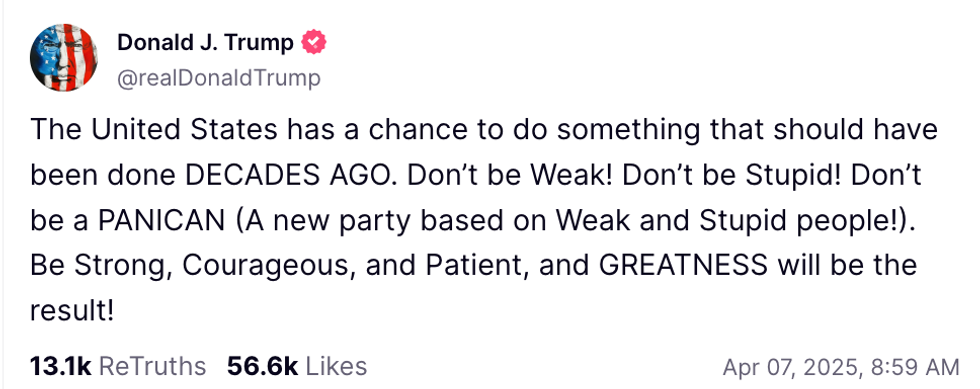 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social