More than half of our known universe is made up a substance scientists can't completely understand: dark matter. Completely undetectable but for the effect it has on normal matter, scientists don't know what dark matter is, or where it is, but they all know it's there. If it wasn't, the universe wouldn't look anything like it does today. For instance, without all that invisible matter's gravity, most galaxies wouldn't contain enough mass to bind them together, and many scientists believed that dark matter was a necessary component in galaxy construction...until now, that is. A new study, published in Nature, reveals the existence of NGC 1052–DF2, a galaxy with almost no dark matter.
A little bit of background...
NGC 1052–DF2 is roughly the size of the Milky Way, but considerably less dense. In fact, it's nearly transparent—astronomers can actually make out other, more luminous galaxies on the other side of it. The researchers estimate the galaxy contains about 1/200th of the stars contained in ours, challenging many scientist's ideas about the nature of the universe. The study's lead researcher, astronomer Pieter van Dokkum, released a statement which read:
We thought that every galaxy had dark matter and that dark matter is how a galaxy begins. This invisible, mysterious substance is the most dominant aspect of any galaxy. So finding a galaxy without it is unexpected. It challenges the standard ideas of how we think galaxies work...
Though strange, the researchers also have some ideas as to how NGC 1052–DF2 came to exist.
Our limited understanding of dark matter didn't forbid the existence of this galaxy, but this is the first we've encountered which continues to exist without it. If NGC 1052–DF2 was a byproduct of a pre-existing galaxy, scientists speculate, it may not have needed dark matter's gravitational pull to help it form. Perhaps if two galaxies collided, jettisoning a huge amount of dust in the same general area, it might be possible. Astrophysicist Katie Mack told Mashable:
It makes sense that that could happen sometimes, that you could have circumstances such that gas is coming together, maybe from an outflow or from some gas falling into a galaxy, and while that gas is coming together through its own gravity, it could fragment and form stars. So, it's not inconceivable
But seriously, why should people care?
Well, for scientists, it answers a crucial question about what dark matter is and how it works. While some scientists imagine it as invisible, intangible matter that just sort of floats around space (somehow), others believed dark matter was just a property of how gravity works when applied on a very, very large scale. It's easier to believe our equations are a bit off than it is to believe 70% of the universe is invisible and undetectable, right?
Well, the truth is stranger than fiction.
This new galaxy suggests dark matter really is a separate and independent entity. After all, if it was a gravitational effect between solar systems or galaxies, it would be in this one as well! It's absence in NGC 1052–DF2 is profound and surprising to many scientific circles.








 Roberto Schmidt/AFP via Getty Images
Roberto Schmidt/AFP via Getty Images


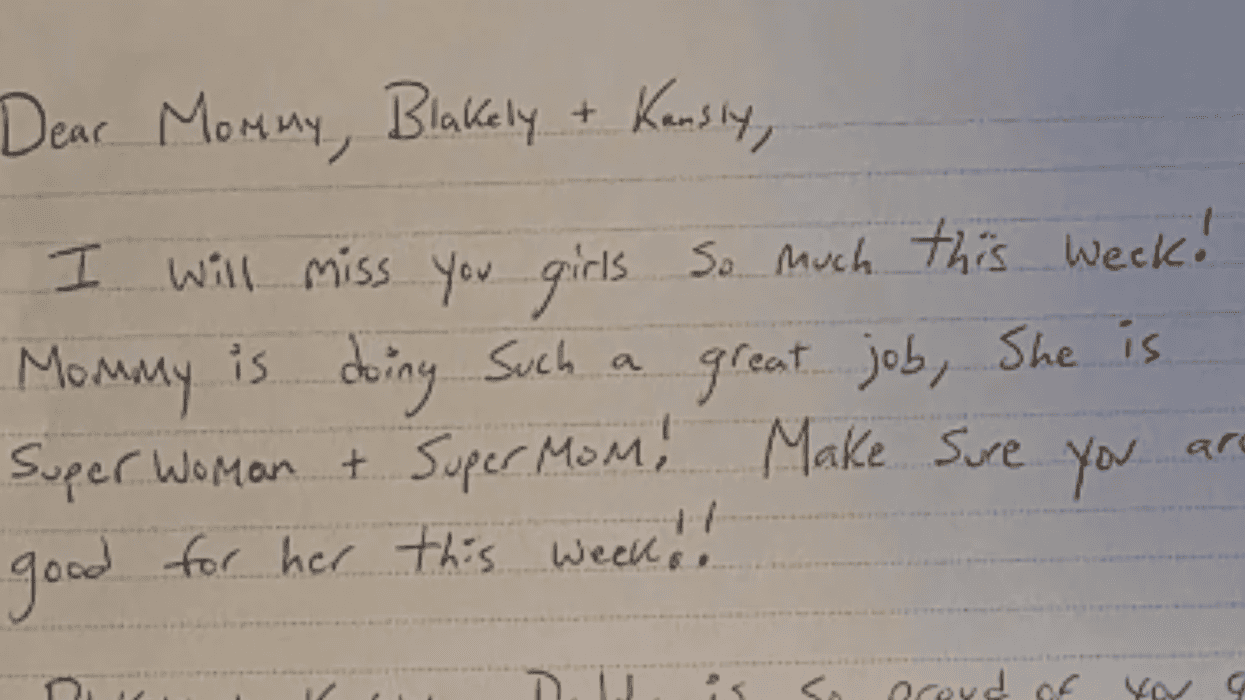


 u/pizzaratsfriend/Reddit
u/pizzaratsfriend/Reddit u/Flat_Valuable650/Reddit
u/Flat_Valuable650/Reddit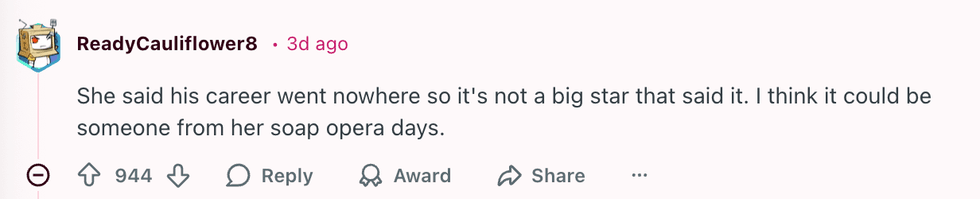 u/ReadyCauliflower8/Reddit
u/ReadyCauliflower8/Reddit u/RealBettyWhite69/Reddit
u/RealBettyWhite69/Reddit u/invisibleshadowalker/Reddit
u/invisibleshadowalker/Reddit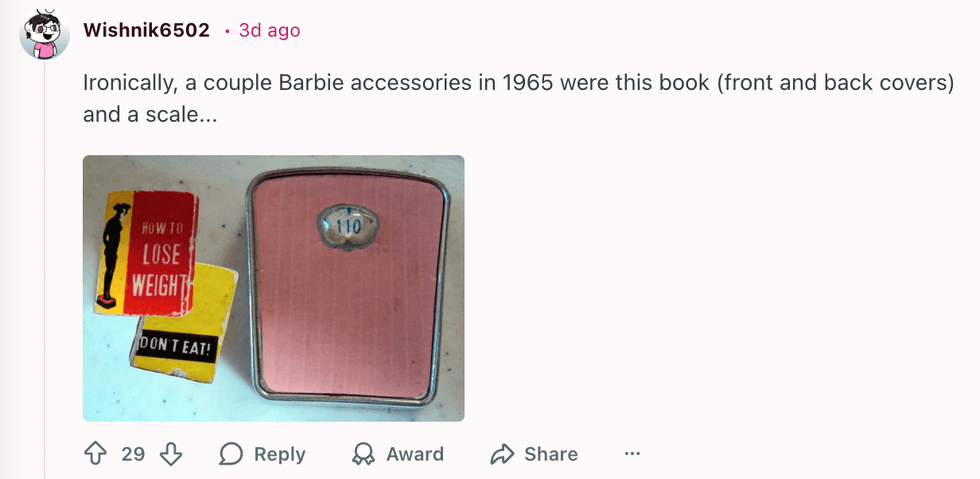 u/Wishnik6502/Reddit
u/Wishnik6502/Reddit u/kateastrophic/Reddit
u/kateastrophic/Reddit u/blking/Reddit
u/blking/Reddit u/SlagQueen/Reddit
u/SlagQueen/Reddit u/geezeslice333/Reddit
u/geezeslice333/Reddit u/meertaoxo/Reddit
u/meertaoxo/Reddit u/crystal_clear24/Reddit
u/crystal_clear24/Reddit u/stinkpot_jamjar/Reddit
u/stinkpot_jamjar/Reddit
 u/Bulgingpants/Reddit
u/Bulgingpants/Reddit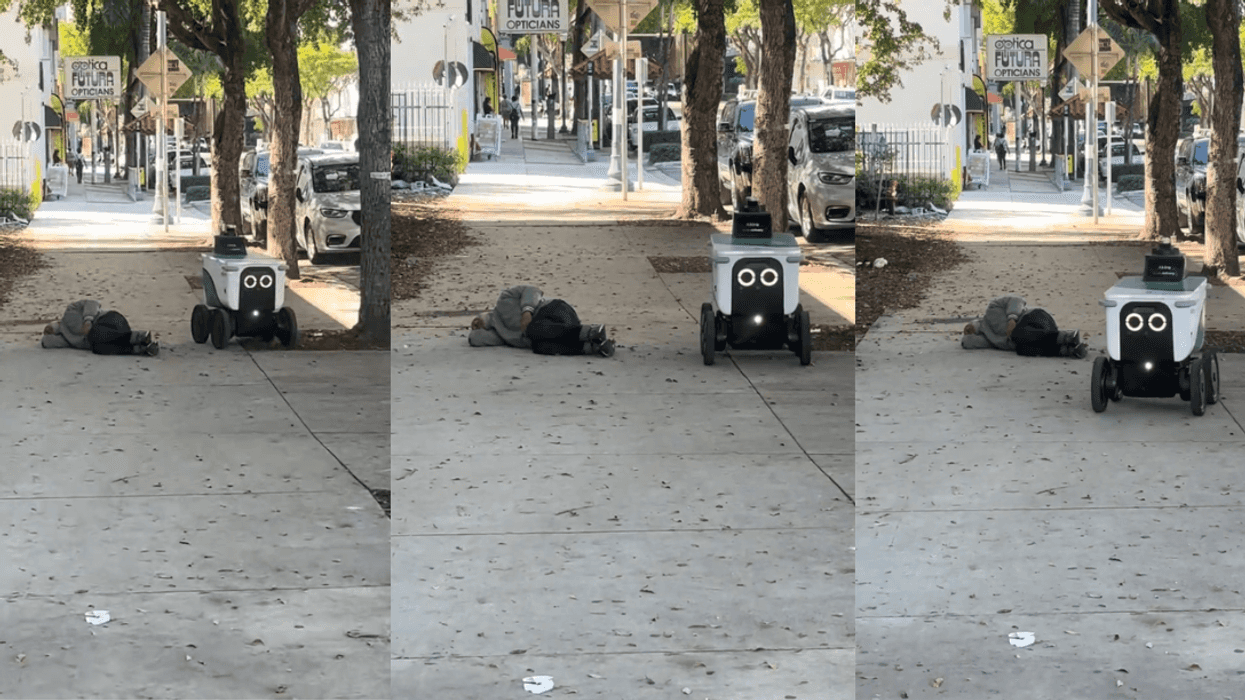
 @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok @hackedliving/TikTok
@hackedliving/TikTok
 @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram @vanderjames/Instagram
@vanderjames/Instagram