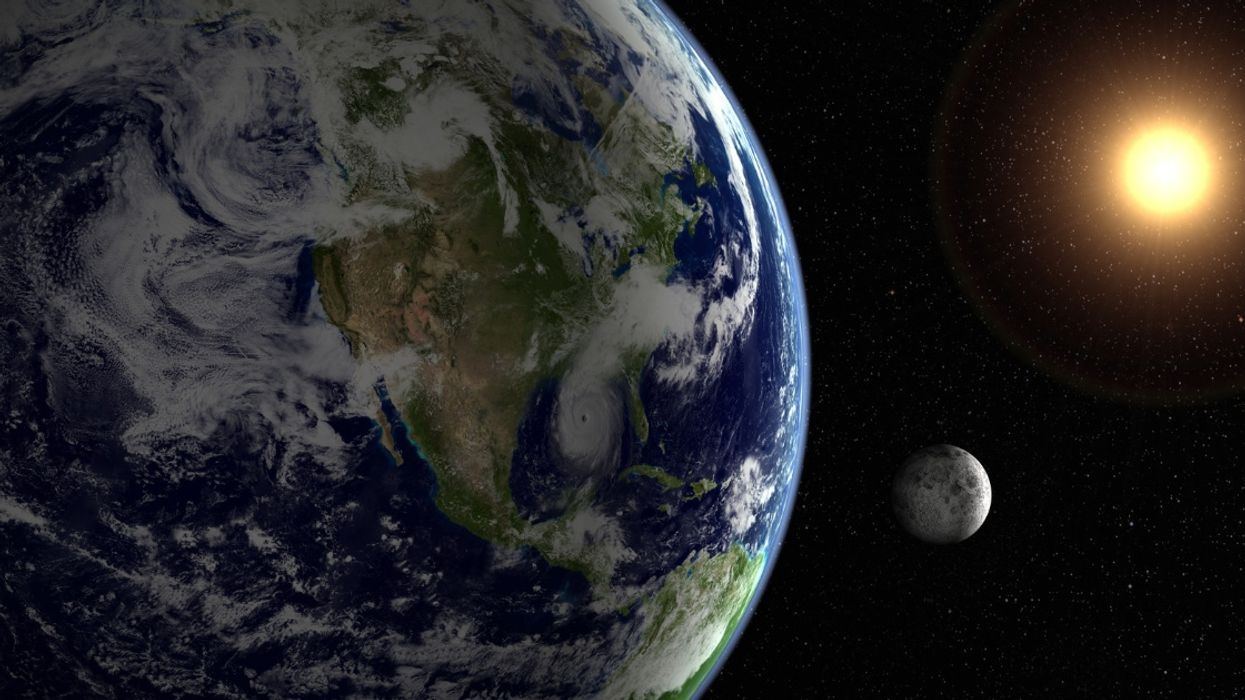
Right now, the northern hemisphere is in the dead of winter, which means it's cold. The winter solstice has just ended, which means it gets dark very early and stays that way far into the morning. And yet, at 2:19 a.m. ET on January 2, Earth slid by the perihelion—the point at which our planet is as close as it gets to the sun.
Earth passes the perihelion every January and the aphelion (the point at which we're farthest away from the sun) every July.
Nottingham Trent University astronomer Daniel Brown joked on Twitter about the perihelion, calling the day's sun a "super sun" (referencing how we call the moon a "super moon" when its at its perihelion).
For those who don't remember from science class, the earth's distance from the sun is constantly changing due to the fact that its orbit isn't circular—it's elliptical, with the sun at one of the ellipse's focal points.
Similarly, though it seems counter-intuitive for the planet to be extra close to the sun just as things are extra cold, Earth's seasons are caused by the tilt of its axis rather than its proximity to heat. During the winter, the northern hemisphere is tipped away from the sun's light, causing winter, while the southern hemisphere is tipped towards, receiving more direct sunlight, which causes summer.
On Twitter, science-fans everywhere were wishing each other a Merry Perihelion!
Meanwhile, Bob Henson, a meteorologist writing for Weather Underground, wrote for Weather Underground that our orbit around the sun isn't completely stable, and our dates of perihelion and aphelion are drifting forward ever so slightly:
"In addition, these date ranges of perihelion and aphelion are also sliding forward on the calendar ever so gradually—less than two days per century—as Earth's tilt itself undergoes a slow-motion wobble. In 13,000 years, perihelion will be arriving in July and aphelion in January."
The sun itself also experiences cycles of activity and non-activity. It's now entering a phase known as the solar minimum, where sun spots fade and the star remains relatively "quiet." This inactivity should come to a "peak" around 2020 before heading back towards a solar maximum in 2024.
Happy Perihelion, everybody! May we grow even closer to the sun next year?
















 Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook @eicathomefinn/Bluesky
@eicathomefinn/Bluesky Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook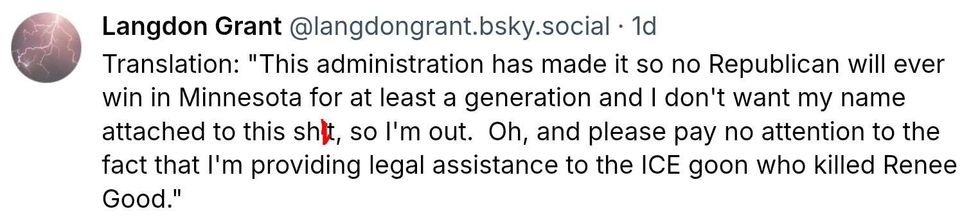 Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook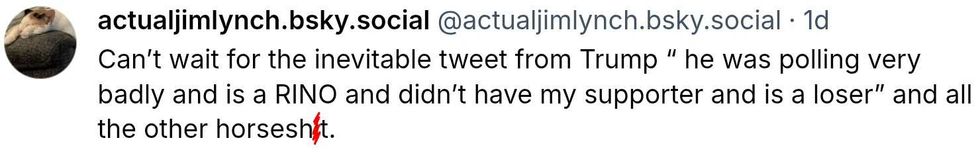 Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook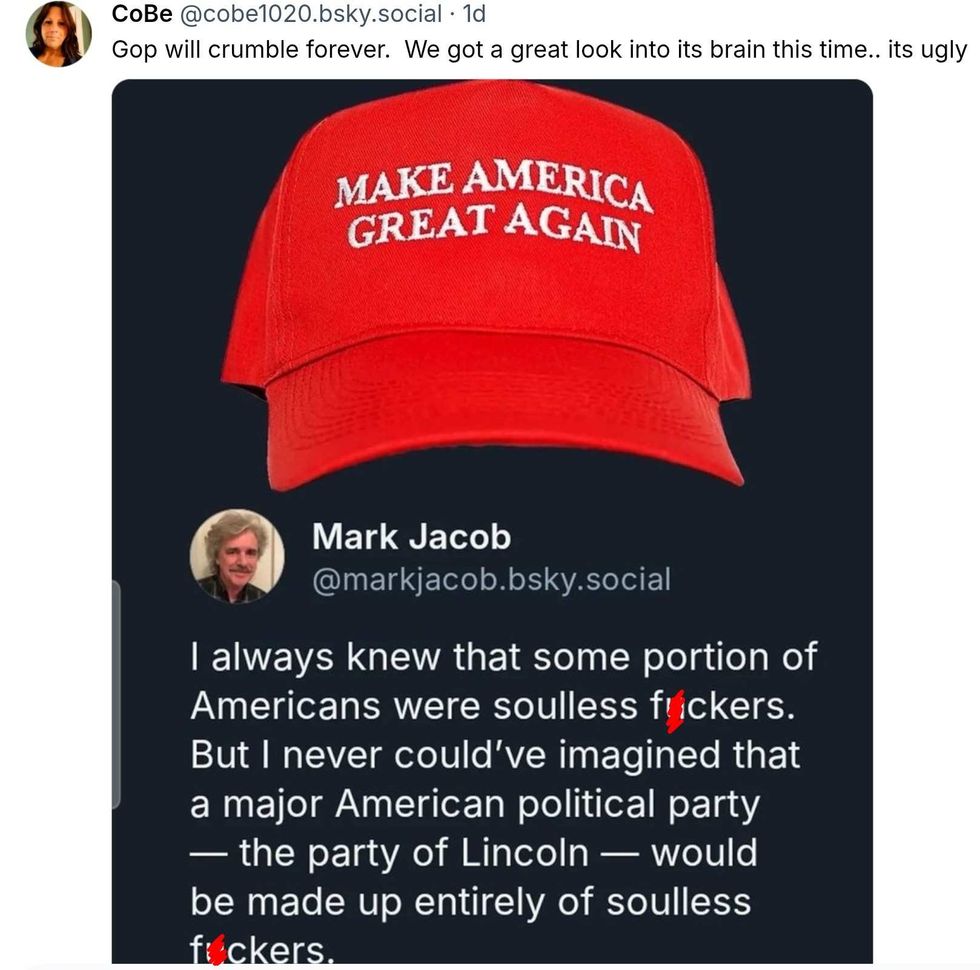 Christina Lorey/Facebook
Christina Lorey/Facebook
 @catmeo28/TikTok
@catmeo28/TikTok @kelcag89/TikTok
@kelcag89/TikTok @andrew_gilstrap/TikTok
@andrew_gilstrap/TikTok @briezeus/TikTok
@briezeus/TikTok @dexx_uppercutt/TikTok
@dexx_uppercutt/TikTok @whoozqueen/TikTok
@whoozqueen/TikTok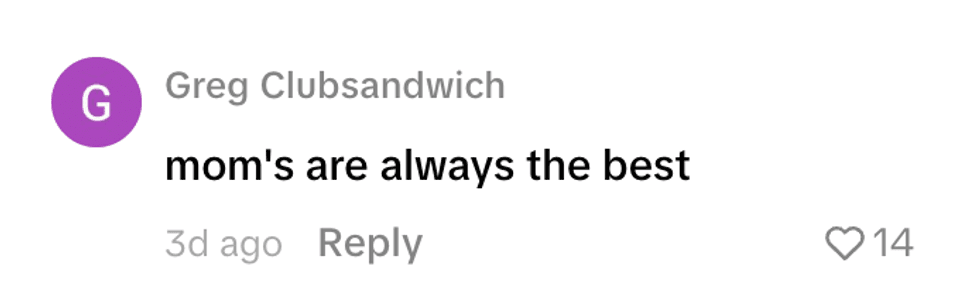 @greg_clubsandwich/TikTok
@greg_clubsandwich/TikTok @amieeetaylor/TikTok
@amieeetaylor/TikTok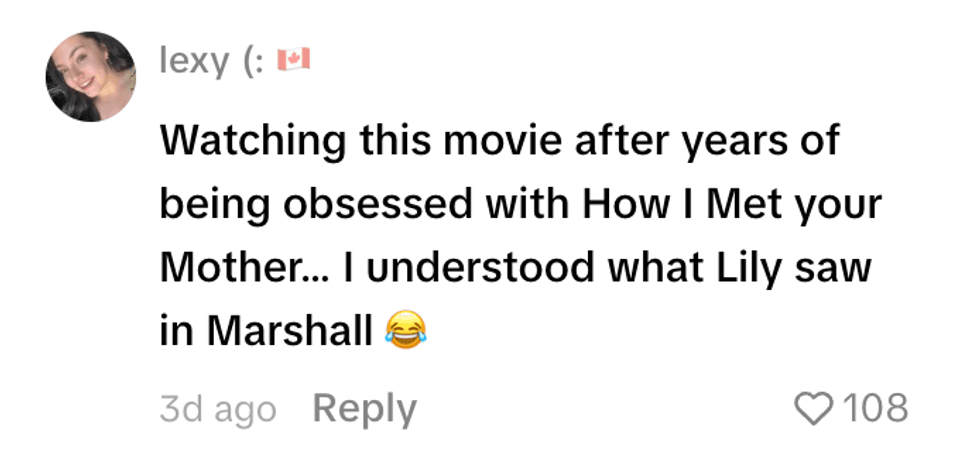 @lexyylee/TikTok
@lexyylee/TikTok @johnnnnnnm6/TikTok
@johnnnnnnm6/TikTok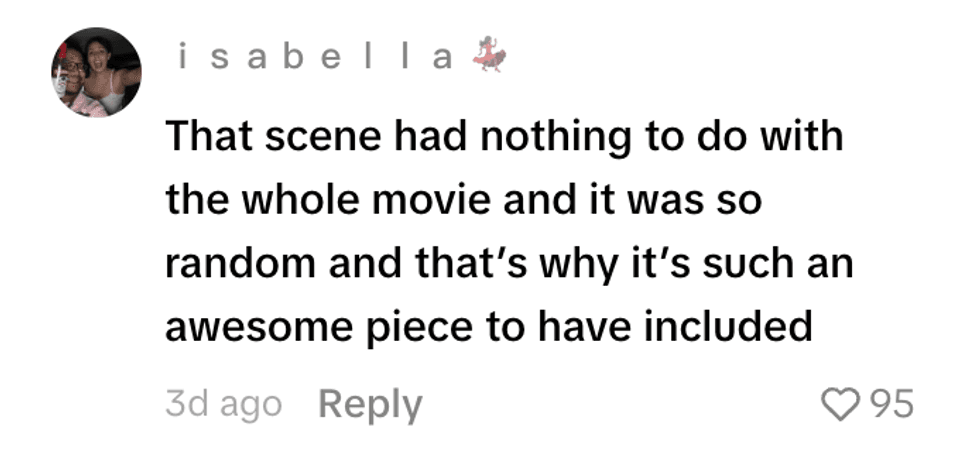 @essencechone/TikTok
@essencechone/TikTok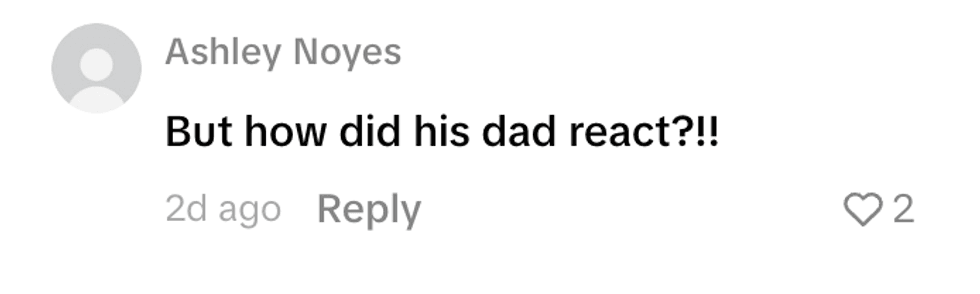 @aksewgnarly/TikTok
@aksewgnarly/TikTok